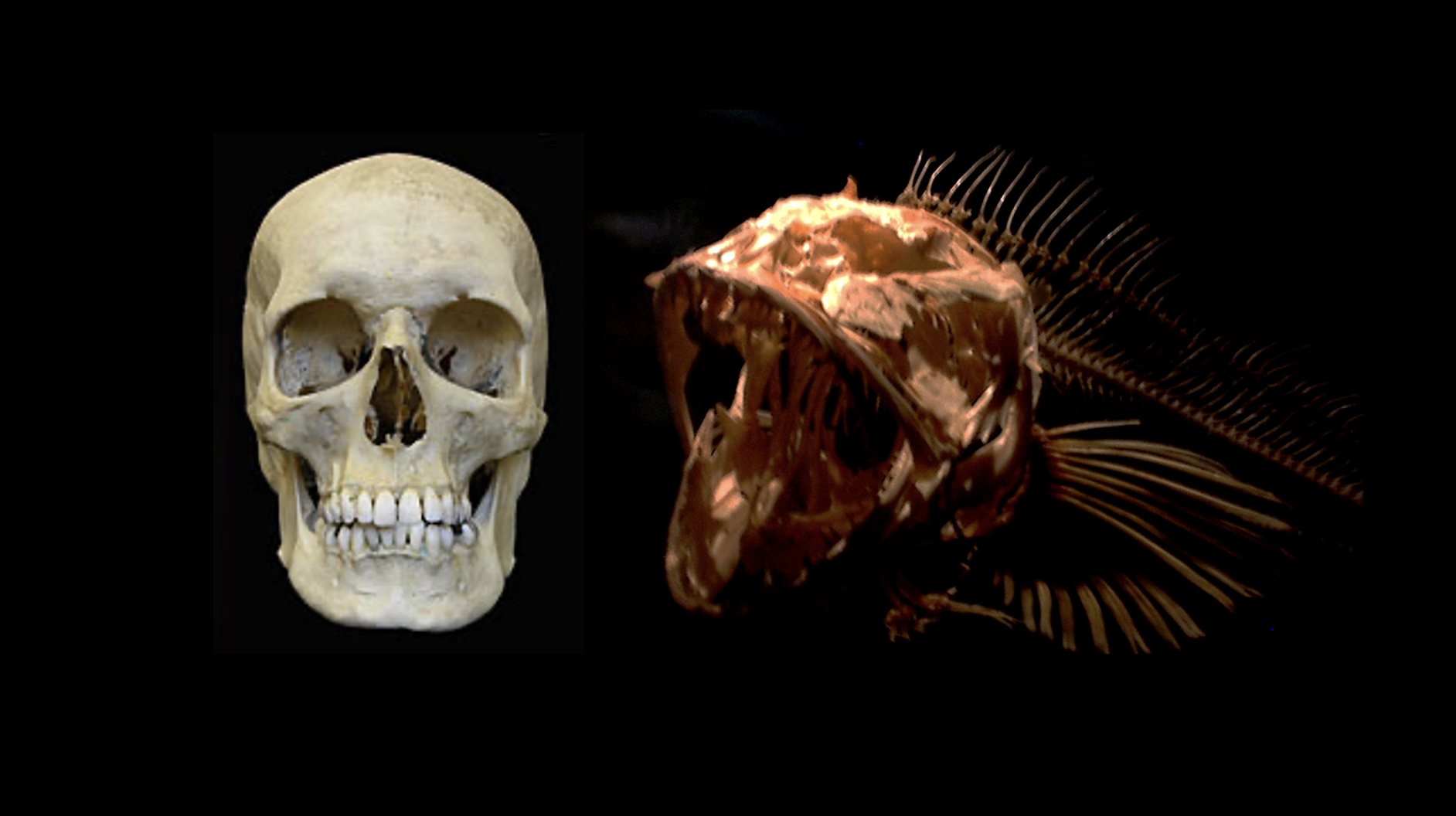
Craniofacial development and disease
The formation of the skull requires the coordinated morphogenesis and growth of numerous structures during development. The fish skull is quite similar to our own. There are differences in pattern and functional adaptations, however the fundamental basis of skull patterning and growth are similar due to stemming from a similar structure in a common ancestor.
In efforts to understand the mechanisms underlying the generation of form, we extend analyses to the development of the skull, including skull roof and jaws. As the general skeletal elements and process of their formation ae shared among vertebrates, we can extend our findings to reveal processes regulating the formation of the skull in human development and underlying causes of disorders. We leverage both unique mutants having craniofacial phenotypes resembling human disorders, but also analysis of patients focusing on inappropriate fusion of the sutures (caniosynostosis), overall size (microcephaly), and proportion of the jaws (microsomia).
We are investigating the genes necessary for coordinated growth and patterning of the skull focusing on genes affecting late development. We are using the zebrafish as a means to functionally dissect the genetic regulation of proportional growth of the skull through forward mutagenesis screens and high-throughput modifier screens of mutants having altered growth and patterning of the skull.
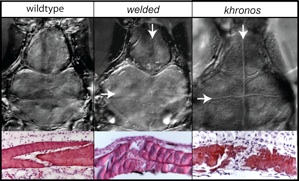
As a component of this work, we are focusing on the development and fusion of the sutures of the skull. The inappropriate fusion of sutures leads to severe birth defects in children. We are using zebrafish mutants that exhibit similar defects in suture development to see if the zebrafish can be used to dissect the genetic regulation of suture patency and bone formation. Additionally, we are investigating whether the zebrafish mutants can act as an experimental model in which to find potential small chemical regulators of suture formation that can prevent precocious suture fusion.
Key Publications
- Henke K, Daane JM, Hawkins MB, Dooley CM, Busch-Nentwich EM, Stemple DL, Harris MP (2017). Genetic regulation of post-embryonic development in the zebrafish: dominant screens affecting form. Genetics. PMID: 28835471
- Alhazmi N, Carroll SH, Kawasaki K, Woronowicz KC, Hallett SA, Trevino CM, Li EB, Baron R, Gori F, Yelick, PC, Harris MP, and Liao EC (2021) Synergistic roles of Wnt Modulators R-spondin2 and R-spondin3 in Craniofacial Morphogenesis and Dental Development. Sci. Reports. Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 12;11(1):5871. PMID: 33712657